The Green Roads for Water Initiative aims to transform the way roads are built and maintained all over the world by incorporating water management and regreening in the design and construction of roads. The aim is to improve livelihoods and resilience of communities living around roads and reduce the negative impacts such as erosion, flooding, sedimentation, and dust while improving the climate resilience of road infrastructure itself and reduce water-related road damage.
We are transforming the way resilient roads are built worldwide
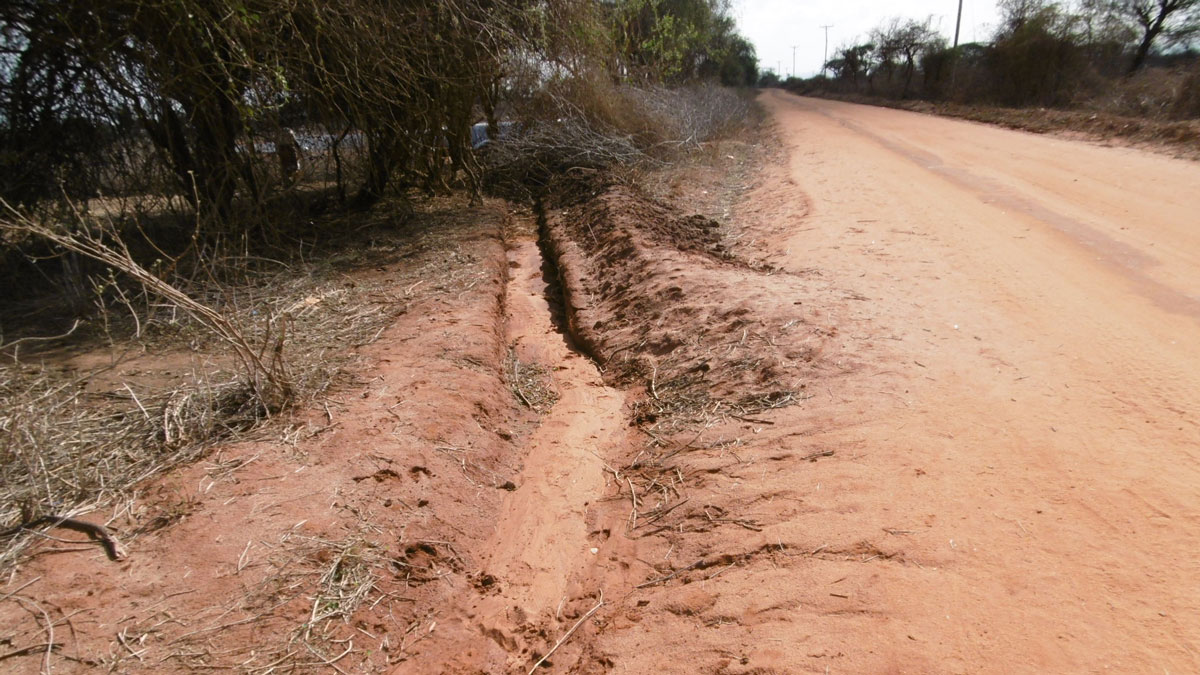
The on-going investment in road building globally is enormous. We have been working over the past years in different geographies and have developed techniques and approaches specific to each geography. Beyond the scope for harvesting water with roads, there is also another compelling argument: if done well, harvesting water with roads will reduce road damage and maintenance needs.
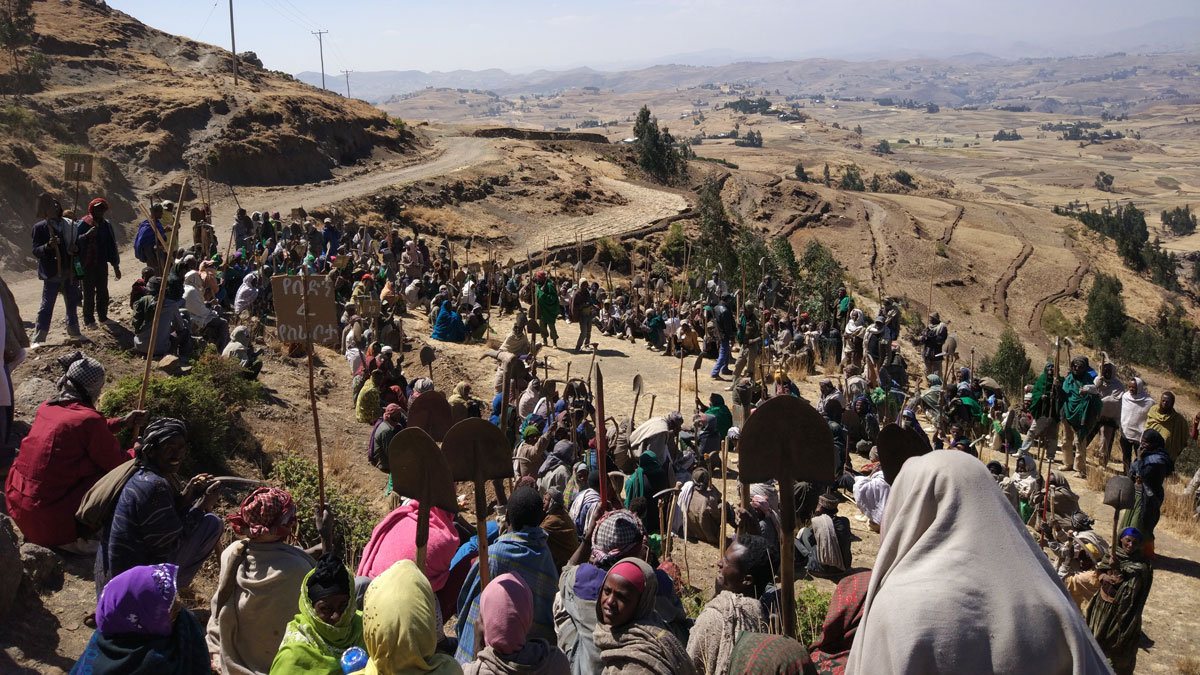
In arid areas, roads can be used to harvest water. The water intercepted by road bodies can be guided to recharge areas or surface storages or applied directly on the land. Roads can also be used to manage water catchments by controlling the speed of runoff, compartmentalizing and mitigating flood runoff, and influencing the sedimentation process in the catchments.
High-altitude catchments present special challenges that require a more intensive integrated landscape approach than is common today. In floodplains and coastal areas, roads play a role in flood protection. Roads often double as embankments and provide evacuation routes and flood shelters. In low-lying wetland areas and floodplains, roads and bridges affect the shallow groundwater tables and have enormous consequences for land productivity.
Roads can improve pastoralist areas for instance by combining the concentrated run-off from roads with planting native grass species. Similarly, the road run-off can be used to rekindle the roots of useful tree species under farmer managed natural re-vegetation programs in very dry areas. Roads can also be used to control sand dune movement or at least not aggravate it.
There is more…
We believe that integrating road and water development where appropriate can also contribute to flood protection, sand harvesting, tree development, nature protection and sand dune control. There are challenges in governance, social access and appropriate techniques, but our experience shows that all these challenges can be overcome.
Learning alliance
The Green Roads for Water Learning Alliance brings together over 800 implementers, researchers, trainers, policymakers, funders and others who work on making roads work for natural resources management and resilience. We encourage you to join, share experience and access training and learning material and join in initiating activities… Read more.